 Optical fibers have been around for nearly 150 years, and the modern use as a means of data transfer goes back as far as 1965. Due to cost and durability they've mostly been confined to servers and intercontinental cables since then, but recently key advances in both the fiber itself and the chips that run it have made it a practical solution for consumer use to extend common formats such as HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort, USB, and more. To find out more about how AOC cables work, and what they can do for you, read on!
Optical fibers have been around for nearly 150 years, and the modern use as a means of data transfer goes back as far as 1965. Due to cost and durability they've mostly been confined to servers and intercontinental cables since then, but recently key advances in both the fiber itself and the chips that run it have made it a practical solution for consumer use to extend common formats such as HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort, USB, and more. To find out more about how AOC cables work, and what they can do for you, read on!
Index:
- What is an Active Optical Cable?
- What is an Optical Cable?
- What makes an AOC "active"?
- How are Active Optical Cables constructed?
- How fast are Active Optical Cables?
- What are Active Optical Cables used for?
- What are the advantages of Active Optical Cables?
- What are the disadvantages of Active Optical Cables?
- What is an SFP port?
More Information:
- USB Info and Guide - DataPro's guide to all things USB
- HDMI Guide and FAQ - Learn more about the HDMI format
- DVI Guide and FAQ - In-depth information on the venerable DVI format
What is an Active Optical Cable?
An AOC (Active Optical Cable) is an optical cable with standard copper interfaces (such as HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort, or USB) on each end. Each connector hood contains a small transceiver that converts electrical signals to optical, and then back on the other end. AOCs typically include copper wires in the cable as well, which provide power to the transceiver at the far end of the cable.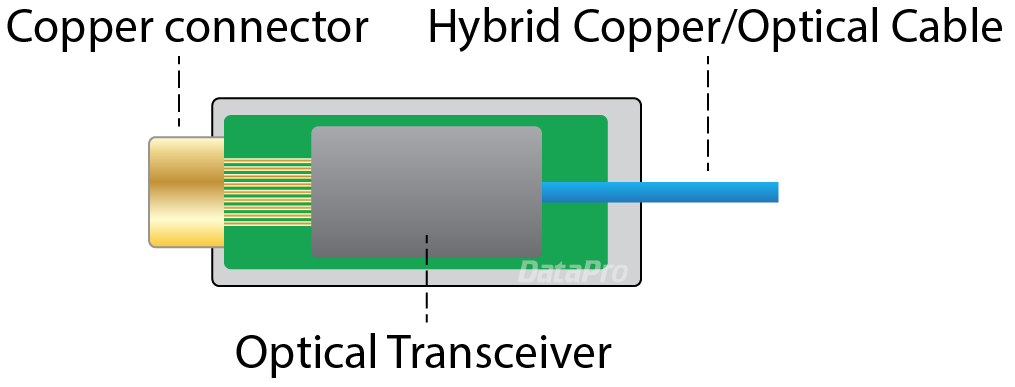
AOCs were originally created for use in datacenters, as an alternative to building optical transceivers into the computer itself as a means of lowering hardware costs. This format also makes the connection more durable, as the optical fiber is permanently installed within the connector. Optical-to-optical connections require extreme precision, and are susceptible to environmental hazards like jostling and dust.
As an alternative to copper cables, AOCs generally have a greater potential length, and resist electromagnetic interference. Their advantage over traditional optical cables is that they require no special interfaces or equipment on the devices involved, and can be used with a multitude of ports and formats.

What is an Optical Cable?
An optical cable is a cable containing one or more optical fibers that carry light. These plastic or glass fibers are sheathed in a reflective material called cladding that ensures no light is lost as it travels down the fiber.Optical cables have a number of desirable characteristics, including an immunity to most types of electromagnetic interference, low latency, high bandwidth, and the ability to operate at much greater lengths than copper cables.
Their downsides have traditionally been durability and cost, but recent developments in materials have improved both.
What makes an AOC "active"?
An "active" cable has electronics embedded in its connectors. These electronics can perform a variety of functions, such as enhancing the data transmission rate of the cable, or in the case of Active Optical Cables, converting the signal to an optical format.There are active non-optical cables as well. For example the electronics in our boosted USB cables serve as a repeater to extend the overall length of the connection.
How are Active Optical Cables constructed?
Each cable typically has a core of 1-2 optical fibers, surrounded by reflective cladding and insulation. Several copper wires run alongside them, providing power to the converter at the far end. Finally, the whole assembly is wrapped in insulation.Each end of the cable contains transceivers that convert data into an optical format for transmission.

How fast are Active Optical Cables?
The fastest it's possible to move data through a fiberoptic cable is somewhere in the Terabit or Petabyte range, depending on the implementation. Since Active Optical Cables are typically intended to replace a traditional copper wire connection, they only need to be as fast as the format they're replacing, which will largely depend on the chipset and transceiver used in the cable.
What are Active Optical Cables used for?
As most consumer electronics do not include any form of optical output, Active Optical Cables are the only way to take advantage of fiber's extended range. They can provide a lightweight and flexible long-distance connection for formats like HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort, USB, and more.In commercial applications, AOCs are often used to connect servers in datacenters. Leaving optical transceivers out of the servers conserves on costs, and allows fiber to be used only where its range and resistance to interference are needed.
What are the advantages of Active Optical Cables?
The primary advantage of AOCs over directly attached optical cables is their universal nature, as they can fit nearly any traditional type of copper connector. Optical fibers must also be precisely aligned at the point of connection, making directly connected optical cables prone to physical disruption. Active Optical Cables have their fiber permanently installed directly to the optical transceiver, making the connection more durable and reliable.Compared to traditional copper cables, Active Optical cables are capable of exponentially longer runs. They also tend to be lighter and thinner, and considerably more resistant to electromagnetic interference.
What are the disadvantages of Active Optical Cables?
The main disadvantage of AOCs is their cost. Even short cables can be many times the cost of a comprable copper or directly attached fiberoptic cable. Depending on the format the AOC is replacing, it may require external power at the source, destination, or both.What is an SFP port?
SFP, or Small Form-Factor Pluggable is an interface format found mostly in data infrastructure equipment such as servers, switches, and routers.SFP consists of a modular port on the device that is meant to accept a transceiver rather than a cable. The transceiver then connects to either copper or fiber as a medium, and is paired with another transceiver at the far end. This solves the issue of supplying power to the transceivers, and gives them fast, direct access to the device. It also allows the use of different SFPs depending on the need for bandwidth, distance, etc.
The SFP format was developed and is maintained by the SNIA (Storage Networking Industry Association). Its interface port is approximately the size of an Ethernet jack, but rectangular and much deeper.
Looking for more information?
If you're looking for a specific solution, feel free to contact our Sales department.
Check out some of our other popular tech guides for even more information:
If you're looking for a specific solution, feel free to contact our Sales department.
Check out some of our other popular tech guides for even more information:






