What is Cat7?
Category 7, or "Cat7" is the designation for a type of Ethernet networking cable. Although first announced in 2002, it has only recently become widely available. What are its applications, and how does it differ from its predecessors? Read on!Index:
Fun fact:
While the specifications of Category 7 have been ratified by the ISO/IEC (International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission), the TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) has ratified Category 6, skipped Category 7 entirely, and then ratified Category 8.
Learn more about networking!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on networking, data cabling,
digital video, and more!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on networking, data cabling,
digital video, and more!
| Cat5 / Cat5e | Cat6 / Cat6a | Cat7 / Cat7a | Cat8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 100-250MHz | 250-500MHz | 600MHz-1GHz | 1-2GHz |
| Max Bandwidth | 1Gbps | 10Gbps | 10Gbps | 40Gbps |
| Max Length | 100m | 100m (50m at 10Gbps) | 100m (50m at 40Gbps) | 30m |
| Shielding | Optional | Optional | Required | Required |
| Year Introduced | 1991 | 1999 | 2002 | 2013 |
What is the difference between Cat5, Cat6, Cat7, and Cat 8?
Essentially, each version is more robust, better shielded, and capable of faster data transmission than its predecessor. For detailed information about each spec, see the table to the right.What does Cat7 mean?
Cat is short for "Category." The transmission rate of an Ethernet cable is measured by frequency (in Hz) and divided into Classes of performance. These "Classes" are served by "Categories" of cable.For example the venerable "Class A" indicates a link of up to 100kHz and is served by "Category 1" cabling -- also known as common telephone wire.
By comparison, the newer "Class F" can operate at frequencies up to 600-1000MHz, and is served by "Category 7" cable -- or Cat7.
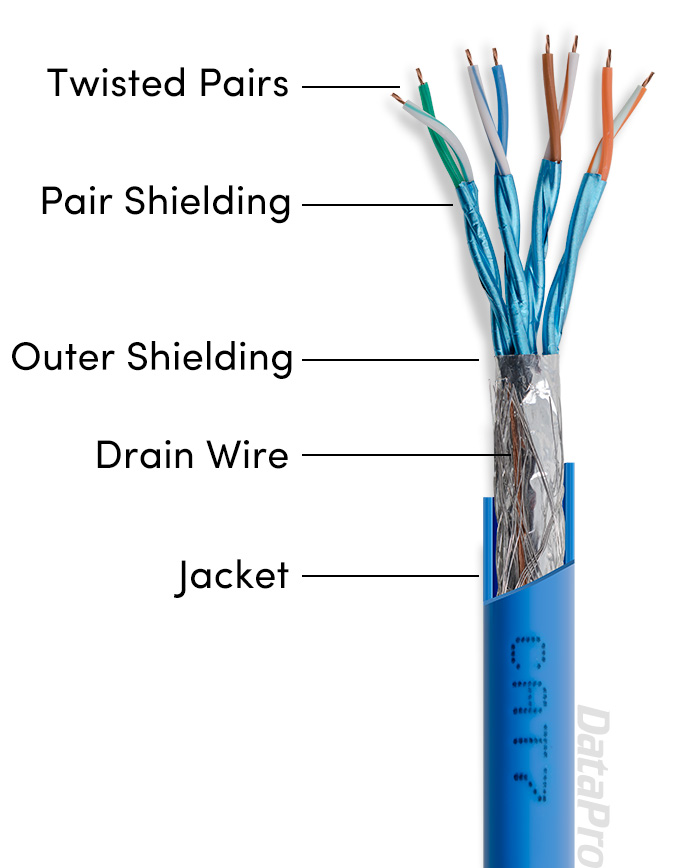
How is Cat7 cable physically different?
Cat7's pairs are individually shielded in addition to a shielded jacket over the whole cable, allowing it to operate at much higher frequencies with less interference. While this level of shielding is available for Cat6 and earlier Ethernet revisions, it is part of the intended design of Cat7.What are the advantages of Cat7?
Although most networking equipment can't take advantage of Cat7a's 40Gbps top speed, Cat7 is useful for making long runs at 10Gbps.Has Cat7 been ratified?
Yes and no. Cat7 was ratified by ISO/IEC (International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission). TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) ratified Cat6a, skipped over Cat7, and ratified Cat8. Regardless of ratification, any cables built to the Cat7 specification should perform similarly.How fast is Cat7?
With compatible network hardware, Cat7 can operate at up to 40Gbps at distances up to 50m, and 10Gbps at lengths up to 100m.Cat7 vs Cat6
Cat7 has stricter specs for crosstalk (interference between conductors) and to achieve this it is required to be fully shielded by default. Such shielding was optional in Cat6 cables. Cat7 also allows the use of TERA style termination hardware - a robust, shielded plug typically used in datacenters and enterprise networking.Cat7 vs Cat7a
Cat7a was an update proposed in 2010 to the Cat7 spec that increased the maximum bandwidth to 40Gbps and the maximum transmission rate to 1GHz. Like Cat7, the category has been ratified by ISO/IEC but not by TIA.Cat7 vs Cat8
Category 8 or Cat8 cable has a maximum bandwidth of 25-40Gbps, with a maximum transmission rate of 2GHz. Cat8's full speed is only available over distances of 16-100' (5-30m), as it is intended to replace fiber for short connections in datacenters and other infrastructure.
Still have questions? Contact us here!
If you've got an cabling question that's stumping you, contact us at the above link.
If you've got an cabling question that's stumping you, contact us at the above link.